SC Operator

"SC" is the new ShapeCollision operator for thinkingParticles
which is meant to replace the "old" ShapeCollision operator.
This all new rigid body solver offers many advantages over the old one
and uses the latest methods and algorithms to calculate rigid body dynamics,
providing faster, more accurate, more efficient and more flexible performance
than the "old" ShapeCollision operator.
To keep backward compatibility with older scenes and files, the old ShapeCollision
is still available from the Dynamics Menu and it produces the exact same
results, as it did in previous versions.
We recommend using this new SC operator instead of the "old" ShapeCollision
The new SC operator offers you the following benefits
Support of multiple Joint types
Enhanced Multi-Threading/Multi-Core support
Specifying Contact Type is no longer needed
Enhanced Solver Algorithm for better full frame sampling
Increased Overall Speed
High Frequency Jittering has been reduced significantly
Voxel Debug Mode added
As a testament to the power that comes with the SC operator, it was
successfully used in the 2010 blockbuster movie 2012
and was instrumental in creating the destruction effects in the various
shots of the movie.
While it is possible to use multiple Shape Collision operators in a DynamicSet, it is highly recommended that you use as few operators of this type as possible. The memory requirements are huge and they increase with each addition of that operator type.
Operator Inputs
ON - (Bool) This input data stream determines whether
the operator is considered 'on' or 'off.' You can connect other operators
to this input channel such as a Bool Helper to activate/deactivate
the whole operator.
Time - (Time) This input data stream is used to define the local
time for the operator when the user wants to override the default system
time.
Floor Node - (Node) This input data stream is used to specify
through a node helper for example a 3D mesh as a floor collision object.
A floor object is automatically treated as immovable with an infinite
mass.
Voxel Grid - (Integer) This input data stream is used to override
the Voxel Grid that is used on the selected particle Group. This value
is normally set within the selected Group's Dynamics
rollout.
Edge Samples - (Integer) This input data stream is used to override
the Edge Samples value that is used on the selected particle Group. This
value is normally set within the selected Group's Dynamics
rollout.
Optimize - (Bool) This input data stream is used to override the
Optimize check box setting that is used on the selected particle Group.
This value is normally set within the selected Group's Dynamics
rollout.
Elasticity - (Scalar) This input data stream is used to override
the Elasticity value that is used on the selected particle Group. This
value is normally set within the selected Group's Dynamics
rollout.
Dynamic Friction - (Scalar) This input data stream is used to
override the Dynamic Friction value that is used on the selected particle
Group. This value is normally set within the selected Group's Dynamics
rollout.
Static Friction - (Scalar) This input data stream is used to override
the Static Friction value that is used on the selected particle Group.
This value is normally set within the selected Group's Dynamics
rollout.
Size As Mass - (Bool) This input data stream is used to override
the Size as Mass check box setting within the Particle Group of Controls.
Floor Voxel Grid - (Integer) This input data stream is used to
override the Voxel Grid spinner value in the Floor Group of Controls within
the Shape Collision Operator.
Important when you set Voxel Grid to 0 (zero) a true box collision is assumed, when set to 1 (one) the mesh itself is used to test the collision to the nearest surface point. The latter mode is much more accurate but it also uses more CPU computing time so it is slower.
Floor Optimize - (Bool) This input data stream is used to override
the Optimize check box setting within the Floor Group of Controls within
the Shape Collision Operator.
Floor Elasticity - (Scalar) This input data stream is used to
override the Elasticity spinner value within the Floor Group of Controls
within the Shape Collision Operator.
Floor Dynamic Friction - (Scalar) This input data stream is used
to override the Dynamic Friction spinner value within the Floor Group
of Controls within the Shape Collision Operator.
Floor Static Friction - (Scalar) This input data stream is used
to override the Static Friction spinner value within the Floor Group of
Controls within the Shape Collision Operator.
OPT Face Threshold - (Angle) This input data stream is used to
override the Face Thresh. spinner value within the Shape Collision Floor
Node.
OPT Edge Threshold - (Angle) This input data stream is used to
override the Edge Thresh. spinner value within the Shape Collision Floor
Node.
OPT Bias - (Scalar) This input data stream is used to override
the Bias spinner value within the Shape Collision Floor Node.
OPT Max Edge Length - (Scalar) This input data stream is used
to override the Max Edge Len. spinner value within the Shape Collision
Floor Node.
OPT Preserve Smooth Boundaries - (Bool) This input data stream
is used to override the Preserve Smooth Boundaries check box setting within
the Shape Collision Floor Node.
OPT NumFaces - (Integer) This input data stream is used to override
the Off Under Faces spinner value within the Shape Collision Floor Node.
Velocity Friction - (Scalar) This input data stream is used to
override the Velocity Friction value that is used on the selected particle
Group as it interacts with the Floor Node. This value is normally set
within the selected Group's Dynamics
rollout.
PHY Collision Iteration - (Integer) This input data stream is
used to override the Collision Iteration spinner value within the Physics
rollout of the Shape Collision Operator.
PHY Contact Iteration - (Integer) This input data stream is used
to override the Contact Iteration spinner value within the Physics rollout
of the Shape Collision Operator.
PHY Deactivation Time - (Scalar) This input data stream is used
to override the Deactiv. Time spinner value within the Physics rollout
of the Shape Collision Operator.
PHY Velocity Threshold - (Scalar) This input data stream is used
to override the Velocity Thresh. spinner value within the Physics rollout
of the Shape Collision Operator.
PHY Rotation Threshold - (Angle) This input data stream is used
to override the Rotation Thresh. spinner value within the Physics rollout
of the Shape Collision Operator.
PHY Activate All - (Bool) This input data stream is used to override
the Activate All check box setting within the Physics rollout of the Shape
Collision Operator.
Operator Outputs
Particle - (Particle) outputs
the current particle information for the colliding particle. Use this
to modify specific particle properties.
Collided - (Bool) this output data stream will return true whenever
a collision is happening. In all other non-colliding situations, the output
will report false as the value.
Collision average Position - (Position) provides the current interpolated
collision point.
Be aware that this point may be highly inaccurate as face to face collisions usually happen on areas and not at one individual point. Also, when objects come into contact and start sliding, the collision point will be generated at all times over and over again.
Collision averaged Normal
- (Normal) outputs the interpolated normal of the calculated collision
point.
Frozen - (Bool) outputs the frozen status of the particles as
determined by and within the Physics
Rollout Menu . When particles are considered "frozen" or
"inactive", this value will be true. When particles are actively
moving, this value will return false.
Double Star = Secondary Initiator Outputs
Double Star Output (**) behaves like the Top-Level Initiator outputs,
this outputs activate connected nodes for evaluation. It is important
to understand that all connected nodes will be evaluated. However, as
this is a secondary Initiator output, it can not be combined with the
Top Level Output at the same time. The main rule still applies: Never
use 2 Initiators on the same node or wiring.
Number of Collisions - (Integer) holds the total number of all
collisions that happened for a particle. A collision may happen multiple
times, especially with sliding objects (surface - surface). Note, this
is a secondary Initiator output that can not be combined
with the top level Initiator outputs at the same time. Either the Top-Level
will be active or the low level department but not both at the same time.
Coll Index - (Integer) outputs the current index number of the
collision. This might be used to get the current progress of the collision
evaluation. Collision index can become as big as the Number of Collisions
value, if this is reached the collisions are done.
Coll Particle A - (Particle) outputs the particle A of the collision
pair. This output is always evaluated before particle B!
Coll Particle B - (Particle) outputs particle B of the collision
pair.
Coll Floor - (Bool) when a collision with the floor object happens,
this output will be set to True.
Coll Position - (Position) outputs the real world position Collision
point.
Coll Normal - (Normal) outputs the normal of the calculated collision
point.
Coll Position A - (Position) outputs the collision position of
Particle A in local object space.
Coll Position B - (Position) outputs the collision position of
Particle B in local object space.
Rollout Menus
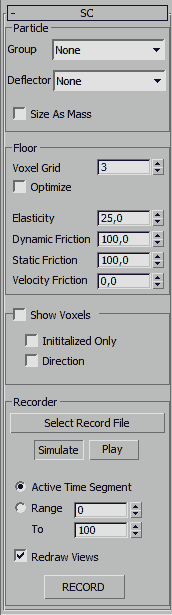
The Shape Collision operator is used to control all true
shape collision dynamics in thinkingParticles.
Particle
Group - this drop-down list
selects the particle collision partners for the floor or inter-particle
collision.
All Physics based parameters are set and controlled within the particle group itself. Select the relevant particle group in the particle group tree view to access the dynamic properties of a particle group.
Deflector - is used to choose the deflector objects. Important: those objects will be treated as unyielding, all the time, regardless of their local physics settings. One application would be to use recorded particles as deflectors.
IMPORTANT
Deflector Particles will use the physics settings from the Floor controls.
Size As Mass - Activate this check box to enable an automatic
mass calculation that is based on the size of the particle. For example,
a particle with a size of 2.0 will be treated as 2 Kg.
Floor
Voxel Grid - This spinner
defines the number of cubic subdivisions to wrap the object's outer boundaries
within.
Important when you set Voxel Grid to 0 (zero) a true box collision is assumed, when set to 1 (one) the mesh itself is used to test the collision to the nearest surface point. The latter mode is much more accurate but it also uses more CPU computing time so it is slower.
Optimize - Activate this check box to enable the parameters
found in the Rollout
Menu. The face count of the colliding meshes will be automatically
reduced. This face reduction is only done "internally" for the
collision objects and not for the rendering mesh. This option may speed
up the dynamic simulation enormously. However, if overdone the results
may be inaccurate.
Elasticity - Use this parameter to control the bounce value between
the floor<->particle collisions. Higher values will make the particles
lose less energy per bounce. Be aware that values greater than 100 will
create extra energy and the particles will gain energy with each bounce.
Dynamic Friction - This spinner sets the friction (you can also
think of it as "power loss") between particles and the floor
when they impact with each other. Please note that this power loss ONLY
happens on impact.
Static Friction - This spinner defines the friction between particles
and the floor when they are in contact (sliding). Higher values will make
the particles slide less.
Velocity Friction - This spinner defines the relative speed difference
between two particles. A slower particle will force a faster one to slow
down. This can be used to simulate viscous substances like molasses.
Show Voxels
Show Voxels - check this
option to enable Voxel debug mode. When on, Voxels will be visible in
the view port as small red dots.
Initialized Only - when checked, initialized Voxels will be shown
as green dots. Initialized Voxels are those Voxels involved in the final
collision detection to find the closest surface point of a colliding partner.
Direction - when checked yellow dots appear on the surface of
the colliding objects indicating the direction of collision based on the
nearest Voxel in space.
Recorder
thinkingParticles allows you to record particle dynamics. It is always
a good idea to use this feature whenever a simulation seems to be perfect
for the job. Recording the particles as they bounce around will make life
easier at a later rendering stage. Playback from hard disk is also usually
much faster than calculating the solution each time you play back the
particle collisions.
Select Record File - Click this button to bring up a standard
Windows Save dialog. Any legal name and path can then be specified to
save the recorded particle simulation.
Simulate, Play, Record - These buttons are fairly self-explanatory.
The Simulate button turns the recorder into playback
mode and will play back the recorded file on hard disk as you scrub the
3ds Max frame slider in the view ports. The Record button
will switch the recorder into record mode. With the record button pressed,
clicking the Play button on the 3ds Max time line will
start the recording and simulation of the particle dynamics. After the
last frame has been reached, the recording automatically stops and turns
into Play mode to show you the results.
Active Time Segment / Range - This is a standard 3ds Max control
that lets you choose whether you want to record the entire particle animation,
or just a specified range of frames as defined within the two spinners.
Redraw Views - when checked, the 3ds Max view ports will be updated
while simulating. Depending on scene complexity it might be a good idea
to turn of View Updates while simulating.
Optimize Rollout
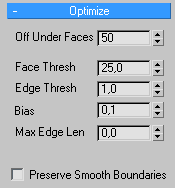
This rollout is responsible for adjusting the degree of optimization for
the particle collisions.
Off Under Faces - If an object that is being sent to be optimized
has fewer faces than the threshold value set in this spinner, it will
not be processed for optimization and ignored. This does not affect it's
participation within the simulation, it simply removes it from the optimization
routines.
Face Thresh - This spinner sets the threshold angle used to determine
which faces are collapsed during the optimization process. Low values
produce less optimization but better approximations of the original shape.
Higher values improve optimization, but are more likely to result in faces
that render poorly as you get more degenerate triangles. (see Bias
below for information on how to control this).
Edge Thresh — This spinner sets a different threshold angle for
open edges (those that bound only one face). A low value preserves open
edges. At the same time you can apply a high Face Threshold value to get
good optimization.
Bias — This spinner's value helps eliminate the skinny or degenerate
triangles that can occur during optimization, which in turn can cause
simulation and rendering artifacts. Higher values keeps triangles from
becoming degenerate. The default of 0.1 is generally considered enough
to eliminate the skinniest triangles, while a value of 0.0 turns the Bias
setting off.
Max Edge Len — This spinner specifies the maximum length beyond
which an edge cannot be stretched when optimized. When Max Edge Len is
0, it has no effect. Any value greater than 0 specifies the maximum length
of the edges. Along with Bias, this control helps you avoid creating long
skinny faces while optimizing.
Preserve Smooth Boundaries — Optimizes an object and maintain
its smoothing. When turned on, allows only faces that share at least one
smoothing group to collapse.
Physics Rollout
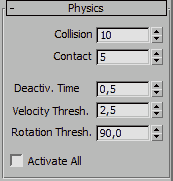
Collision Iteration - This spinner sets the number of sub-steps
to be used to estimate the real collision point of colliding objects.
The lower this number, the faster the simulation will run. However, lower
values would also mean less accurate results. In most situations, you
can keep this value between 5-10, while in exceptionally complex scenes,
you can try to set a value as high as 30 to get more accuracy.
Contact Iteration - This spinner defines the number of sub-steps
to be used between colliding objects to create a "contact" situation.
Face to face contact is one of the most complex situations to handle for
the dynamics engine. Increase this value to get more realistic simulations.
Deactivation Time - This spinner defines the time-slot in which
a particle is surveyed to determine whether it is actively moving due
to dynamics or simply performing a stupid "dynamics dance" as
it comes to rest. If a particle falls into this time-slot and it's speed
or rotational value is equal or below the ones defined, it is considered
sleeping or frozen. Lower values will freeze the particles much faster.
This spinner works in concert with the two spinners below it (Velocity
Thresh. and Rotation Thresh.).
Velocity Threshold - This spinner sets the minimum speed an object
needs to fall below to become treated as frozen or inactive. Be aware
that other objects interacting with a sleeping one may change this status
when the impact creates a velocity higher than this value.
Rotation Threshold - This spinner sets the minimum rotational
speed and object needs to fall below to become treated as frozen or inactive.
As is the case with the Velocity Threshold, be aware that other objects
interacting with a sleeping one may change this status when the impact
creates an angular velocity higher than this value.
Activate All - This check box will "wake up" frozen
fragments after they have been deactivated either by
Velocity Threshold or Rotational Threshold. This setting can be helpful
when working with fragments, since frozen particles don't respond to space
warps.